

The error parameters in the CBD area resulted to be between 15 to 45% higher than those of the Nairobi city wide area for the six global DEMs, thus providing further insights into the contribution of building heights to errors in global DEMs. This methodology was also applied to the Central Business District (CBD) area of Nairobi, characterized by taller buildings and high building density. Our findings show that the removal of building density error resulted in the improvement of the vertical height accuracy of the global DEMs of up to 45% for MERIT and 40% for ALOS. The six DEMs were corrected by deriving a linear relationship between building density and DEM error. Our results show building error at highest building density varying between 1.25 m and 5.07 m for the DEMs used, with the MERIT DEM showing the smallest vertical height error from the reference DEM. This methodology was applied to Nairobi, Kenya using six global DEMs (SRTM, MERIT, ALOS, NASADEM, TanDEM-X 12 m, and TanDEM-X 90 m DEM). In this research we developed a methodology for building error correction that can be applied to any other case study, where building density data and a local reference DEM data are available. Despite recent advances in developing vegetation corrected DEMs, the effect of building height and density errors in global DEMs in urban areas are still poorly understood, and their correction remains a challenge. Urban flood models that use Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) to simulate extent and depth of flood inundation rely on the accuracy of DEMs for predicting flood events. Moreover, it outlines that such analyses are also possible by using time-saving cloud-computing platforms. The proposed research shows that the combined use of the two above-mentioned DEMs and appropriate filtering methods allows an effective description of 3D changes. All adopted filtering strategies improve the results reliability albeit the third one is the most effective in mountainous, urban and rural areas. Three different statistical approaches, i.e., Limit of Detection, Uniformly Distributed Error and Probability Map, were compared to avoid artifacts propagating further. Such a product was affected by many of Tukey's outliers, subsequently cleaned out. After recognizing AW3D30 (version 3.2) and NASA SRTM DEM (version 3) as the optimal DEM combination, their DEM of Differences was computed.
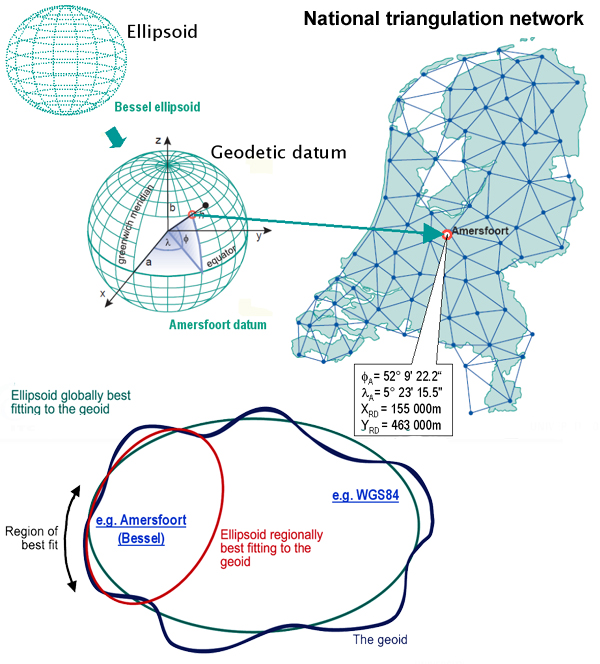
#Horizontal datum code
To achieve these goals, a Javascript code in Google Earth Engine (GEE) environment was developed. The aim of this paper is: i) to explore global DEMs feasibility in detecting 3D changes at the global scale and ii) to examine the impact of filtering propagated error on 3D changes. Because of the large amount of data and the vertical accuracy inhomogeneity, their applicability in defining three-dimensional changes of large areas is not predictable. Nonetheless, high-resolution DEMs are not available for the whole Earth and, when not at disposal, open-source, medium-resolution, global DEMs may be a relevant source of knowledge. The optimal dataset must be selected according to the environmental phenomenon under investigation as the offered resolution strongly affects the information level. This unique database will provide basic data for research on the physical processes and socioeconomic activities related to these lakes and their basins in China and expect to feed a broad user community for their application in different areas.ĭigital Elevation Models (DEMs) represent the geospatial dataset core needed to model 3D changes. It covers 767 lakes (>10 km²) in China and their basin extent associating with 34 variables organized into five categories: Hydrology, Topography, Climate, Anthropogenic, and Soils.
The CODCLAB is available in three data formats, including raster layers (Level 1) in “tiff” format, vector shapefiles (Level 2), and attribute tables (Level 3). To facilitate stakeholders obtaining comprehensive data of lake basins in China, we compiled the comprehensive data set for China’s lake basins (CODCLAB) mostly from publicly available data sources based on spatial analysis and mathematical statistics methods in this study. Therefore, assessments of lacustrine ecosystems require the spatial and temporal characteristics of key physical and human-dimensional attributes for lakes and lake basins. Nevertheless, climate changes and anthropogenic interventions remarkably altered lake and basin hydrology in recent decades, which pose a significant threat to lacustrine ecosystems.

Lakes provide water-related ecosystem services that support human life and production.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
